
APA Style
Hrittick Saha, Bonhi Dey, Khan Rajib Hossain. (2025). Hydrogel-based Biosensors in Biomedical Applications. Biomaterials Connect, 2 (Article ID: 0024). https://doi.org/Registering DOIMLA Style
Hrittick Saha, Bonhi Dey, Khan Rajib Hossain. "Hydrogel-based Biosensors in Biomedical Applications". Biomaterials Connect, vol. 2, 2025, Article ID: 0024, https://doi.org/Registering DOI.Chicago Style
Hrittick Saha, Bonhi Dey, Khan Rajib Hossain. 2025. "Hydrogel-based Biosensors in Biomedical Applications." Biomaterials Connect 2 (2025): 0024. https://doi.org/Registering DOI.
 ACCESS
Review Article
ACCESS
Review Article
Volume 2, Article ID: 2025.0024

Hrittick Saha
hrittick0416@student.nstu.edu.bd

Bonhi Dey
bonhi0917@student.nstu.edu.bd

Khan Rajib Hossain
apexlabbd2@mails.ucas.ac.cn
1 Department of Applied Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Noakhali Science and Technology University, Chattogram 4310, Bangladesh
2 Environmental science and disaster management, Noakhali Science and Technology University, Chattogram 4310, Bangladesh
3 Department of Natural Science, BGMEA University of Fashion and Technology, Dhaka 1230, Bangladesh
4 State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed
Received: 18 Jun 2025 Accepted: 15 Dec 2025 Available Online: 31 Dec 2025
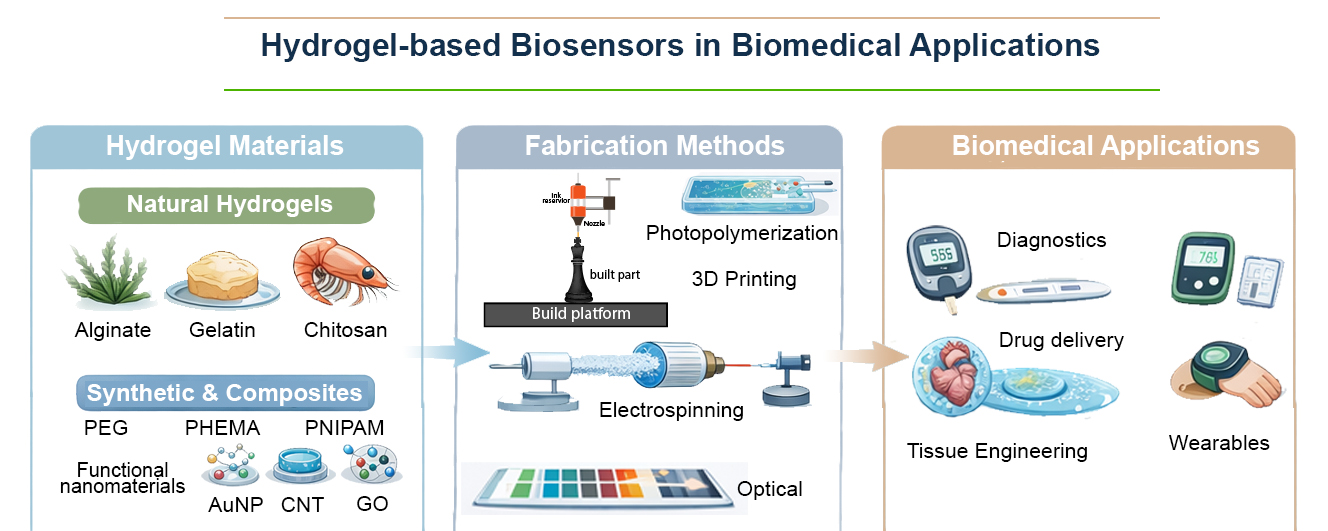
Hydrogels have great potential for applications due to their high water content and unique 3D interconnected structure. Due to their excellent biocompatibility, tunable dynamic characteristics, and sensitive responses to environmental stimuli, including temperature, pH, and ions, hydrogels are an ideal material platform for new biosensors. While synthetic hydrogels can achieve precise control of structure and function through chemical or physical methods to meet the needs of various applications, hydrogel has the advantages of abundant resources and green environmental protection. Wearable medical devices have advanced significantly. The electrochemistry of anti-pollution hydrogels or optical transmission platforms can be used to detect high-level tumor markers, and the functionalization of conductive hydrogels can lead to new methods for heart tissue engineering and nerve repair. The most recent developments in sensor design, material selection, and manufacturing techniques were overviewed, along with their potential applications across various domains and the challenges that remain in achieving stability, sensitivity, and clinical translation.
Disclaimer : This is not the final version of the article. Changes may occur when the manuscript is published in its final format
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies. Learn more