
APA Style
Avanish Kumar, G.L. Devnani, Dan Bahadur Pal. (2025). Sustainable Degradation of Organic Pollutants Using Various Treatment Processes: A Review. Sustainable Processes Connect, 1 (Article ID: 0018). https://doi.org/Registering DOIMLA Style
Avanish Kumar, G.L. Devnani, Dan Bahadur Pal. "Sustainable Degradation of Organic Pollutants Using Various Treatment Processes: A Review". Sustainable Processes Connect, vol. 1, 2025, Article ID: 0018, https://doi.org/Registering DOI.Chicago Style
Avanish Kumar, G.L. Devnani, Dan Bahadur Pal. 2025. "Sustainable Degradation of Organic Pollutants Using Various Treatment Processes: A Review." Sustainable Processes Connect 1 (2025): 0018. https://doi.org/Registering DOI.
 ACCESS
Review Article
ACCESS
Review Article
Volume 1, Article ID: 2025.0018

Avanish Kumar
akumarch@hbtu.ac.in

G.L. Devnani
gldevnani@hbtu.ac.in

Dan Bahadur Pal
dbpal@hbtu.ac.in
Department of Chemical Engineering, Harcourt Butler Technical University, Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, 208002, India
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed
Received: 27 May 2025 Accepted: 24 Oct 2025 Available Online: 27 Oct 2025
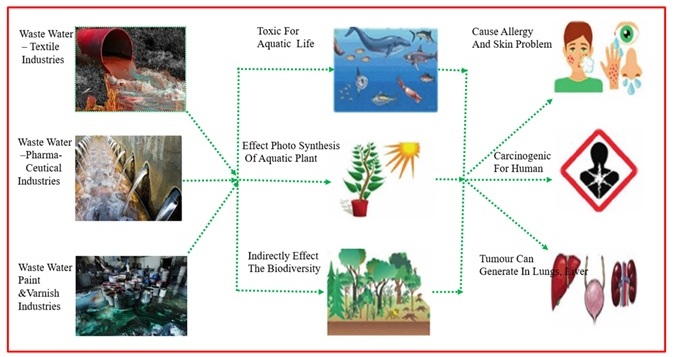
Organic pollutants such as dyes or colorants are water-soluble compounds produced by various industries, including textiles, food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, printing inks, paints, leather, and plastics. Dyes are of particular concern because their stable aromatic structures make them toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic to living organisms. Therefore, environmental scientists have focused on developing various physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes to remove these contaminants from wastewater. The conventional techniques such as coagulation, flocculation, precipitation, photocatalytic degradation, ion exchange, and membrane filtration have been widely adopted. More recently, biomass-based waste materials such as bagasse, green algal biomass, and household vegetable and agricultural residues have been investigated as promising, low-cost, and sustainable adsorbents for dye removal. In addition, nanomaterials such as zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, silica powder, carbon nanotubes, and well-structured biocomposite materials have also shown great potential in wastewater treatment. The present review not only emphasizes a detailed study of essential treatment technologies but also highlights their merits and limitations in a structured manner, supported by comparative tables and illustrative figures.
Disclaimer : This is not the final version of the article. Changes may occur when the manuscript is published in its final format.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies. Learn more